(For a selected publications see below or go to Google Scholar.)
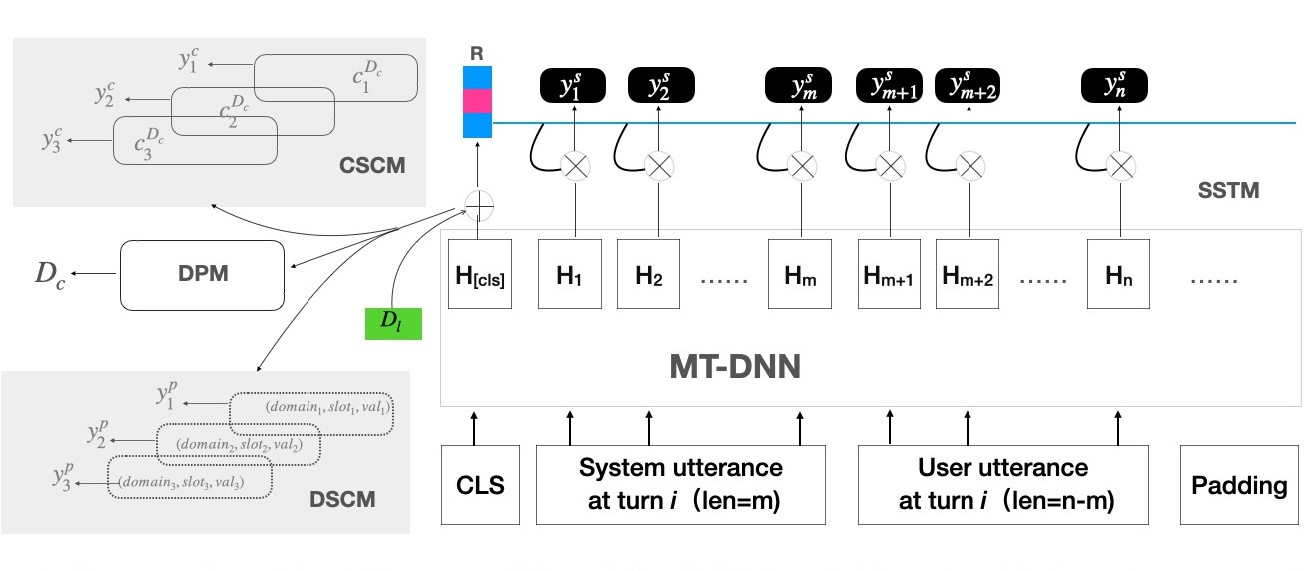
Wang D., Lin C., Zhong L., and Wong KF.
We present a fast and scalable architecture, in which we incorporate both classification based and extraction-based approaches and then elaborately design four modules to jointly extract dialogue states. Experimental results on MultiWoz2.0 validate the superiority of our proposed model in terms of complexity and scalability when compared with state-of-the art methods, especially in multi-domain dialogues entangled with many turn utterances.
Peng X., Lin C., and Stevenson M.
Based on the robust ℓ1 norm goodness-of-fit criterion, we propose a simple post-processing step to improve CLWEs. It is fully agnostic to the training process of the original CLWEs and can therefore be applied widely. Extensive experimental results based on bilingual lexicon induction and cross-lingual transfer for natural language inference tasks show that our method substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
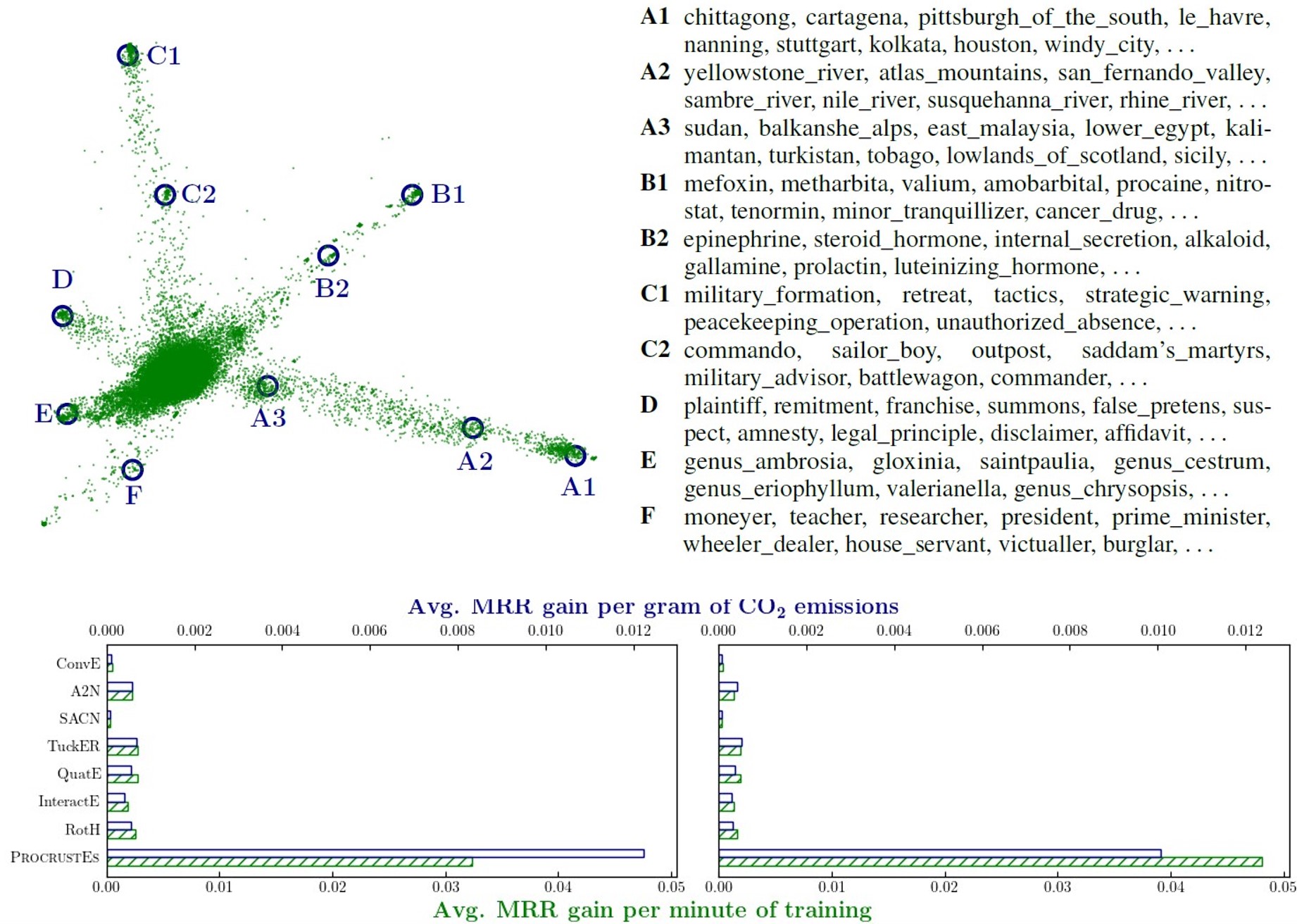
Peng X., Chen G., Lin C., and Stevenson M.
We propose a simple yet effective KGE framework which can reduce the training time and carbon footprints by orders of magnitudes compared with state-of-the-art approaches, while retaining competitive performance. We highlight three technical innovations, namely full batch learning via relational matrices, closed-form Orthogonal Procrustes Analysis for KGEs, and non-negative-sampling training. In addition, as the first KGE method whose entity embeddings also store full relation information, our trained models encode rich semantics and are highly interpretable.
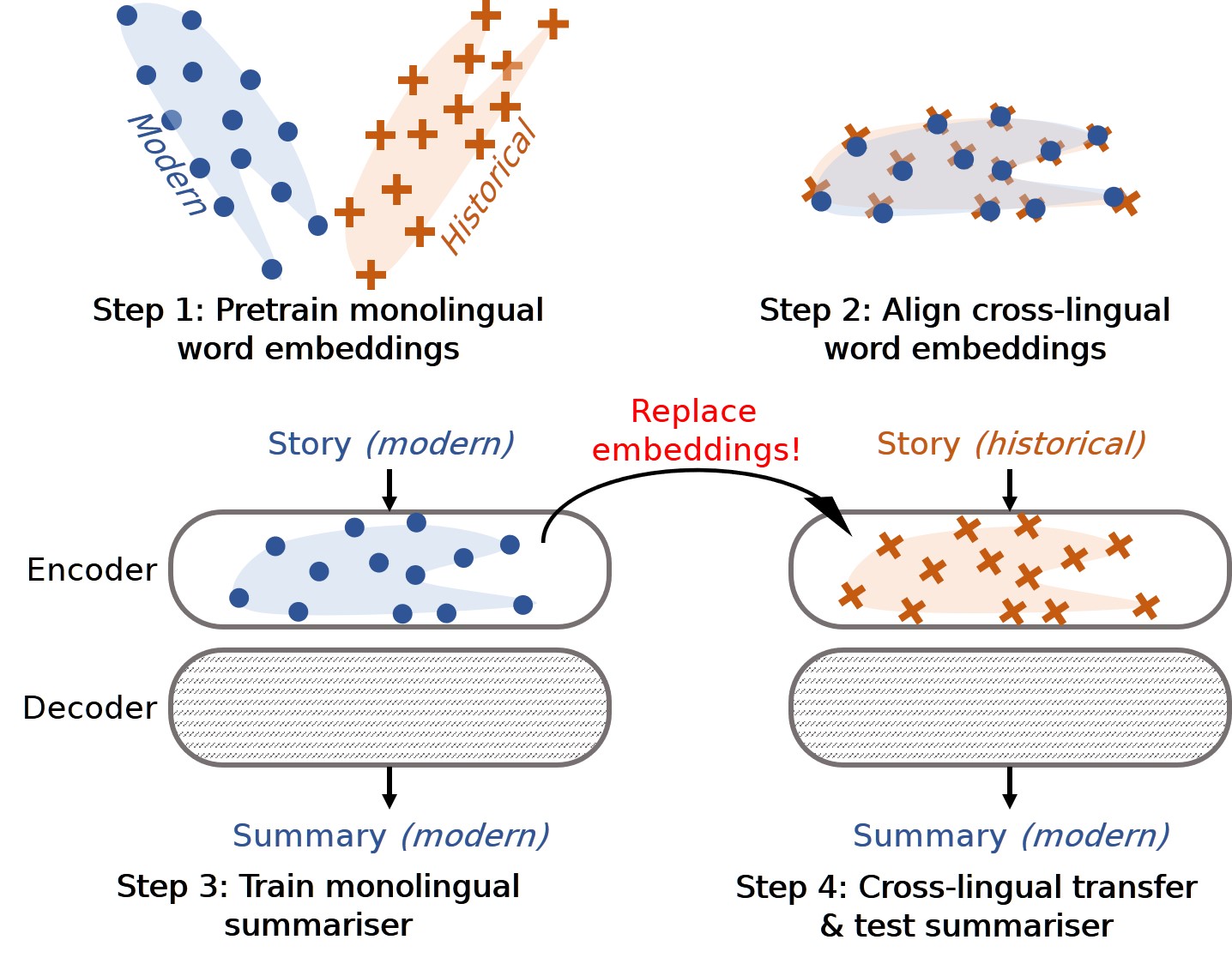
Peng X., Zheng Y., Lin C., and Siddharthan A.
We propose a hitherto unexplored and challenging task of historical text summarisation. To kickstart research in this field, we construct a high-quality summarisation corpus for historical German and Chinese, with modern German and Chinese summaries by experts. We also propose a model for historical text summarisation that does not require parallel supervision and provides a validated high-performing baseline for future studies.
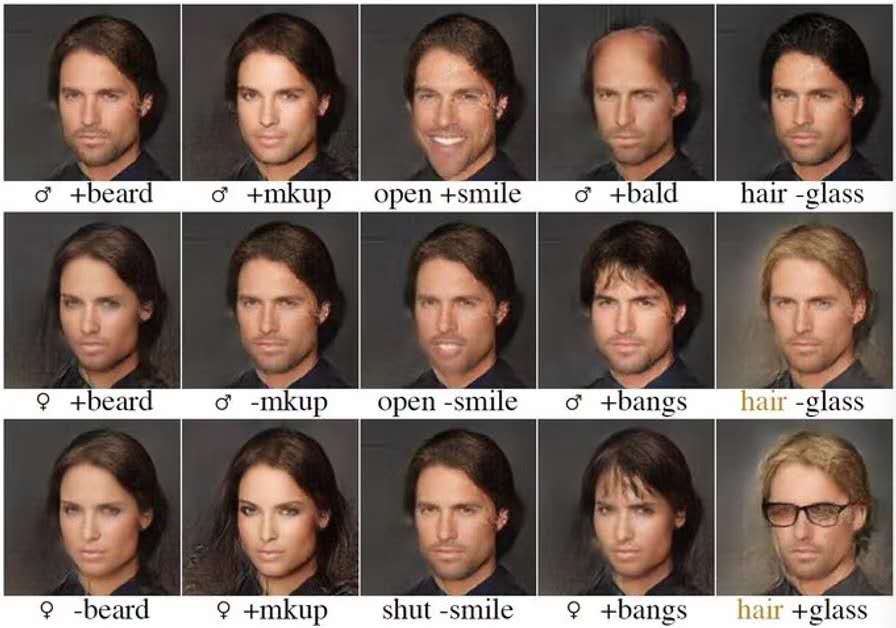

Li X., Lin C., Li R., Wang C., and Guerin F.
We tackle the problem disentangling the latent space of an autoencoder in order to separate labelled attribute information from other characteristic information. This then allows us to change selected attributes while preserving other information. Our method, matrix subspace projection, is much simpler than previous approaches to latent space factorisation, for example not requiring multiple discriminators or a careful weighting among their loss functions.
Li X., Chen G., Lin C. and Li R.
We propose DGST, a novel and simple Dual-Generator network architecture for text Style Transfer. Our model employs two generators only, and does not rely on any discriminators or parallel corpus for training. Both quantitative and qualitative experiments on the Yelp and IMDb datasets show that our model gives competitive performance compared to several strong baselines with more complicated architecture designs.
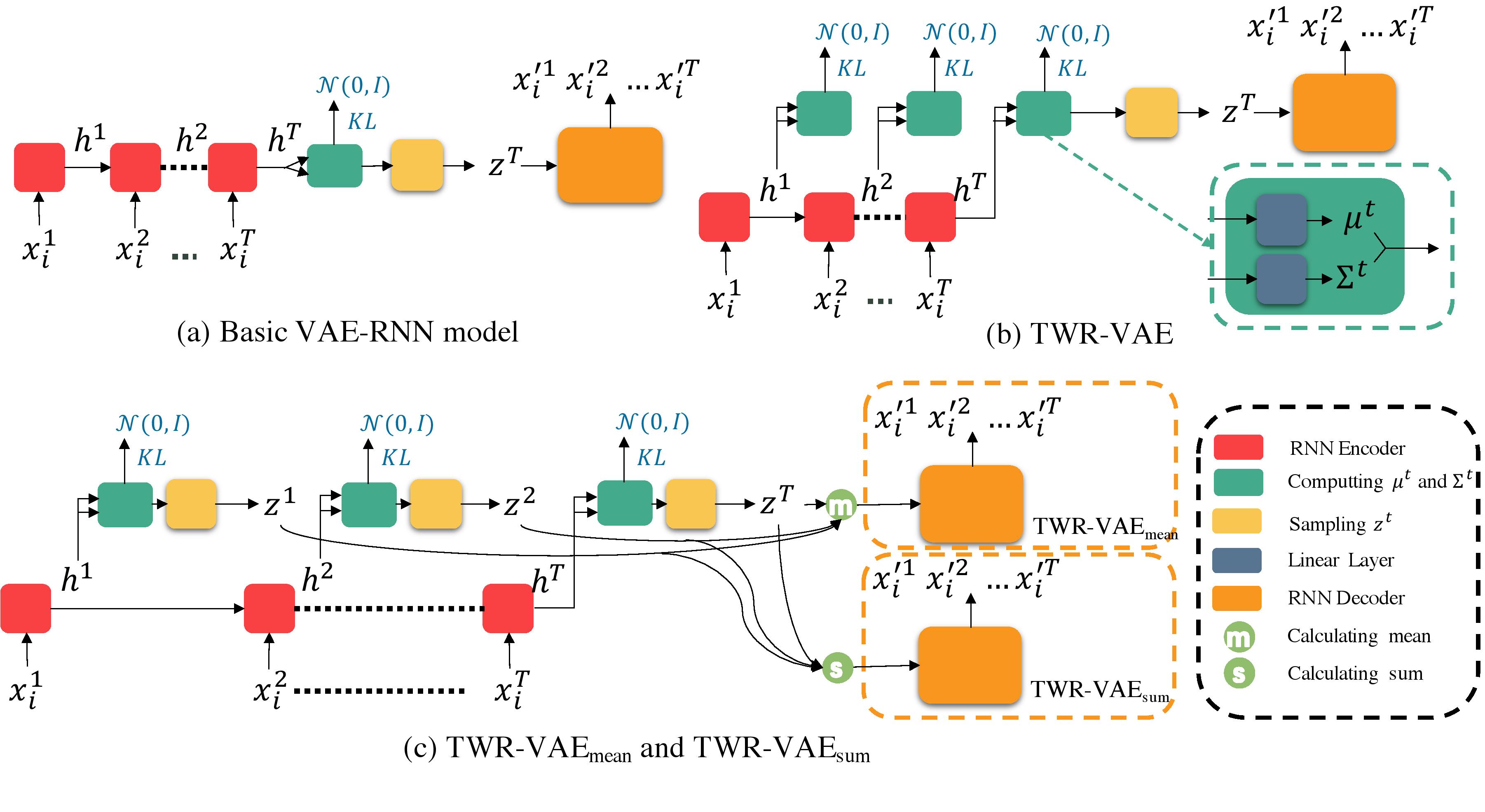
Li R., Li X., Chen G. and Lin C.
In this paper, we propose a simple, generic architecture called Timestep-Wise Regularisation VAE (TWR-VAE), which can effectively avoid posterior collapse and can be applied to any RNN-based VAE models. The effectiveness and versatility of our model are demonstrated in different tasks, including language modelling and dialogue response generation.

Mao R., Lin C. and Guerin F.
End-to-end training with Deep Neural Networks (DNN) is a currently popular method for metaphor identification. However, standard sequence tagging models do not explicitly take advantage of linguistic theories of metaphor identification. We experiment with two DNN models which are inspired by two human metaphor identification procedures. By testing on three public datasets, we find that our models achieve state-of-the-art performance in end-to-end metaphor identification.

Li R., Lin C., Collinson M., Li X. and Chen G.
Recognising dialogue acts (DA) is important for many natural language processing tasks such as dialogue generation and intention recognition. In this paper, we propose a dual-attention hierarchical recurrent neural network for DA classification. Our model is partially inspired by the observation that conversational utterances are normally associated with both a DA and a topic, where the former captures the social act and the latter describes the subject matter.
Li R., Li X., Lin C, Collinson M. and Mao R.
In this paper, we present a new architecture called Full-Sampling-VAE-RNN, which can effectively avoid latent variable collapse. Compared to the general VAE-RNN architectures, we show that our model can achieve much more stable training process and can generate text with significantly better quality.
(Best Paper Award Runner-up)

Mao R., Lin C. and Guerin F.
In this paper, we propose an unsupervised learning method that identifies and interprets metaphors at word-level without any preprocessing, outperforming strong baselines in the metaphor identification task. Our model extends to interpret the identified metaphors, paraphrasing them into their literal counterparts, so that they can be better translated by machines. We evaluated this with two popular translation systems for English to Chinese, showing that our model improved the systems significantly.
Fast and Scalable Dialogue State Tracking with Explicit Modular Decomposition
Wang D., Lin C., Zhong L., and Wong KF.
NAACL 2021
Cross-Lingual Word Embedding Refinement by ℓ1 Norm Optimisation
Peng X., Lin C., and Stevenson M.
NAACL 2021
Highly Efficient Knowledge Graph Embedding Learning with Orthogonal Procrustes Analysis
Peng X., Chen G., Lin C., and Stevenson M.
NAACL 2021
Summarising Historical Text in Modern Languages
Peng X., Zheng Y., Lin C., and Siddharthan A.
EACL 2021
Latent Space Factorisation and Manipulation via Matrix Subspace Projection
Li X., Lin C., Li R., Wang C., and Guerin F.
ICML 2020
DGST: a Dual-Generator Network for Text Style Transfer
Li X., Chen G., Lin C. and Li R.
EMNLP 2020
Improving Variational Autoencoder for Text Modelling with Timestep-Wise Regularisation
Li R., Li X., Chen G. and Lin C.
COLING 2020
Listener’s Social Identity Matters in Personalised Response Generation
Chen G., Zheng Y. and Du Y.
INLG 2020
Dialogue State Tracking with Pretrained Encoder for Multi-domain Trask-oriented Dialogue Systems
Wang D., Lin C., Zhong L. and Wong KF.
arXiv 2020
Revisiting the linearity in cross-lingual embedding mappings: from a perspective of word analogies
Peng X., Lin C., Stevenson M. and Li C.
arXiv 2020
End-to-End Sequential Metaphor Identification Inspired by Linguistic Theories
Mao R., Lin C. and Guerin F.
ACL 2019
A Dual-Attention Hierarchical Recurrent Neural Network for Dialogue Act Classification
Li R., Lin C., Collinson M., Li X. and Chen G.
CoNLL 2019
A Stable Variational Autoencoder for Text Modelling
Li R., Li X., Lin C, Collinson M. and Mao R.
INLG 2019 (Best Paper Award Runner-up)
Generating Quantified Descriptions of Abstract Visual Scenes
Chen G., van Deemter K. and Lin C.
INLG 2019
Word Embedding and WordNet Based Metaphor Identification and Interpretation
Mao R., Lin C. and Guerin F.
ACL 2018
SimpleNLG-ZH: a Linguistic Realisation Engine for Mandarin
Chen G., van Deemter K. and Lin C.
INLG 2018
Modelling Pro-drop with the Rational Speech Acts Model
Chen G., van Deemter K. and Lin C.
INLG 2018
Incorporating Constraints into Matrix Factorization for Clothes Package Recommendation
Wibowo A., Siddharthan A., Masthoff J. and Lin C.
UMAP 2018
Automatically Labelling Sentiment-bearing Topics with Descriptive Sentence Labels
Barawi M., Lin C., and Siddharthan A.
NLDB 2017 (Best Paper Award)
Extracting and understanding contrastive opinion through topic relevant sentences
Ibeke E., Lin C., Wyner A. and Barawi M.
IJCNLP 2017
Sherlock: a Semi-Automatic Framework for Quiz Generation Using a Hybrid Semantic Similarity Measure
Lin C., Liu D., Pang W. and Wang Z.
Cognitive Computation, Springer, 2015
Sentiment-Topic Modelling in Text Mining
Lin C., Ibeke E., Wyner A. and Guerin F.
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2015
Hete-CF: Social-Based Collaborative Filtering Recommendation Using Heterogeneous Relations
Luo C., Pang W., Wang Z. and Lin C.
ICDM 2014
HetPathMine: A Novel Transductive Classification Algorithm on Heterogeneous Information Networks
Luo C., Guan R., Wang Z. and Lin C.
ECIR 2014
Dynamic Joint Sentiment-Topic Model
He Y., Lin C., Gao W. and Wong K.
TIST 2013
Feature LDA: a Supervised Topic Model for Automatic Detection of Web API Documentations from the Web
Lin C., He Y., Pedrinaci C. and Domingue J.
ISWC 2012
Automatically Extracting Polarity-Bearing Topics for Cross-Domain Sentiment Classification
He Y., Lin C. and Alani H.
ACL 2011
A Comparative Study of Bayesian Models for Unsupervised Sentiment Detection
Lin C., He Y. and Everson R.
CoNLL 2010
Joint Sentiment/Topic Model for Sentiment Analysis
Lin C. and He Y.
CIKM 2009 (CIKM 2020 Test of Time Award)